In today’s rapidly evolving world, the traditional classroom model is gradually giving way to innovative learning environments that foster creativity, collaboration, and hands-on problem-solving skills. Maker Spaces, equipped with makerspace furniture and cutting-edge tools and resources, are revolutionizing K12 education across America. These spaces empower students to become active learners, while also preparing them for the demands of the future workplace. This blog post explores how Maker Spaces are transforming learning in K12 schools and the critical role furniture plays in supporting these dynamic environments.
Maker Spaces: Empowering Students for Future Success
- Fostering Creativity and Innovation: Makerspaces provide students with the freedom to explore their imaginations and unleash their creative potential. In these environments, students engage in open-ended projects, allowing them to brainstorm ideas, prototype, and iterate. According to a study by the New Media Consortium (NMC), Maker Spaces promote divergent thinking, enhancing students’ ability to generate innovative solutions, a skill highly sought after in the workplace of the future (citation 1).
- Cultivating Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills: Through hands-on experiences and real-world challenges, Maker Spaces cultivate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Students encounter obstacles, experiment with different approaches, and learn from their failures. This iterative process helps them develop resilience, adaptability, and analytical thinking abilities that are essential for success in a rapidly changing job market (citation 2).
- Encouraging Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaboration is a key driver of success in the modern workplace. Maker Spaces promote collaborative learning, allowing students to work together, share ideas, and solve problems as a team. By engaging in group projects, students develop effective communication, leadership, and teamwork skills, which are highly valued in today’s collaborative work environments (citation 3).
Makerspace Furniture: Creating Supportive Environments for Makerspaces
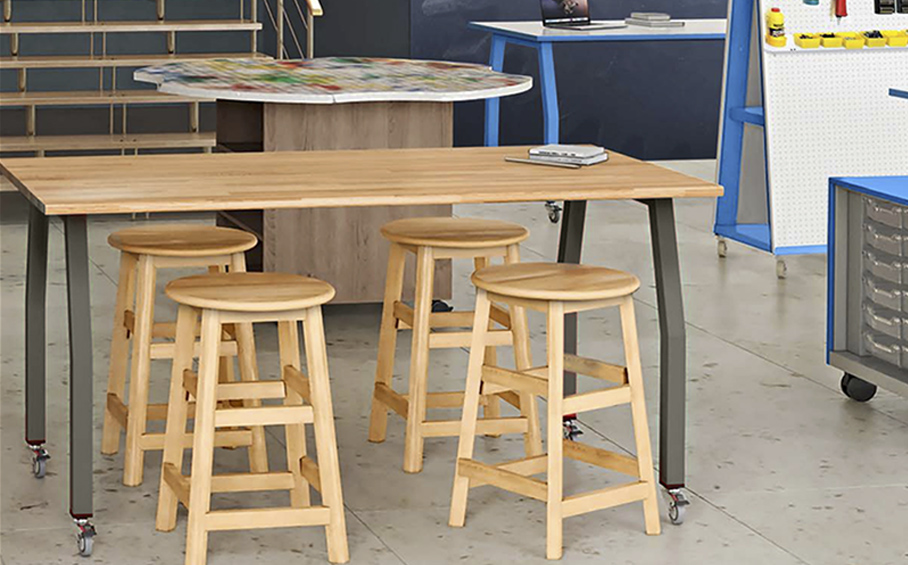
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The furniture in Makerspaces plays a pivotal role in creating flexible and adaptable learning environments. Modular furniture, such as configurable tables and mobile storage units, enables students to reconfigure the space based on project requirements. This flexibility fosters collaboration, experimentation, and the seamless integration of different learning modalities (citation 4).
- Ergonomics and Comfort: Comfortable and ergonomically designed furniture in Maker Spaces ensures that students can work for extended periods without discomfort or distractions. Adjustable chairs and workstations promote proper posture and reduce physical strain, allowing students to focus on their projects and maximize their productivity (citation 5).
- Storage and Organization: Well-designed furniture with ample storage options helps maintain a clean and organized Maker Space. Storage solutions such as shelving units, drawers, and cabinets enable students to store and access tools, materials, and prototypes easily. This promotes efficiency, reduces clutter, and encourages a sense of responsibility for maintaining a tidy and functional learning environment (citation 6).
Maker Spaces have emerged as transformative learning environments that equip students with the skills and mindsets required for success in the future workplace. By fostering creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving abilities, these spaces empower students to become lifelong learners and innovators. The role of furniture cannot be underestimated in supporting these dynamic environments. Flexible, ergonomic, and well-organized furniture creates an environment that facilitates collaboration, adaptability, and seamless engagement with hands-on projects. As K12 schools continue to embrace the Maker Movement, the thoughtful integration of furniture will play a crucial role in shaping future-ready students.
Citations:
- New Media Consortium (NMC). (2017). NMC/CoSN Horizon Report: 2017 K-12 Edition.
- Partnership for 21stCentury Learning. (2015). P21 Framework Definitions. Retrieved from
- Johnson, L., Adams Becker, S., Cummins, M., Estrada, V., Freeman, A., & Ludgate, H. (2016). NMC/CoSN Horizon Report: 2016 K-12 Edition.
- Fadel, C., Bialik, M., & Trilling, B. (2015). Four-Dimensional Education: The Competencies Learners Need to Succeed. Center for Curriculum Redesign.
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Office Ergonomics: Your How-To Guide.
- Education Week. (2018). Creating Successful Makerspaces in Schools.